Think Highers Ultimate Guide to Cannabis Distillates
The extraction and distillation of cannabinoids has come quite a long way since its outbreak just a few years ago.
Simple extraction techniques were well-practiced by many people in the past.The state-of-the-art extraction of today’s world, however, is anything but simple. 
Distillation is one of the oldest extraction processes. More recently, distillation has begun making waves across cannabis extraction industries. It is speculated that cannabis distillates are the future cannabis extract.
What exactly are these cannabis distillates? And more importantly, why is it superior to regular cannabis extract?
What Is The Definition Of Distillate?
Distillation is scientifically defined as the purification of substances through a collection of heating and then cooling methods. The distillation’s end product is called a distillate.
 Distillation yields a cleaner and purer end concentrate in cannabinoid extracts than most of the other extraction techniques.
Distillation yields a cleaner and purer end concentrate in cannabinoid extracts than most of the other extraction techniques.
In actual fact, most researchers and enthusiasts seldom refer to the final product of the distillation of cannabinoids process, as the “The Pure.”
That’s because, even though the cannabinoids have been extracted via a hydrocarbon solvent, the final distillate product is “solvent-free”, meaning it has zero parts-per-million residual solvent.
The distillate products are one of the most effective and diverse types of cannabis and hemp extracts available within the market.
What are Cannabinoid Distillates?
Top class extraction practitioners use the process of distillation to extract only the specific compounds found in the original material.
It is possible to majorly distill only CBD or THC from a hemp or cannabis plant, respectively.

Cannabis distillates are not as pure as cannabinoid isolates, for they are not as refined.
Various cannabinoids, valuable molecules and minor contaminants (terpenes and flavonoids) may still be present in cannabis distillates. It can be referred to as a precursor to isolates because it could be further refined even more to isolate a specific cannabinoid.
Research has found that the cannabinoids profiles found in distillates and remaining beneficial molecules can be highly beneficial for the body.
For example, CBD Distillates usually contain THC of some amount, which could render it as illegal in some states, whereas an isolate-based CBD contains no trace amounts of THC.
Moreso, it should be known that most distillates and other extracts, produced for improved THC effectiveness are grown from the raw marijuana plant.
In contrast, the CBD distillate is extracted, mostly, from the cultivation of hemp plants.
Hemp vs. Cannabis
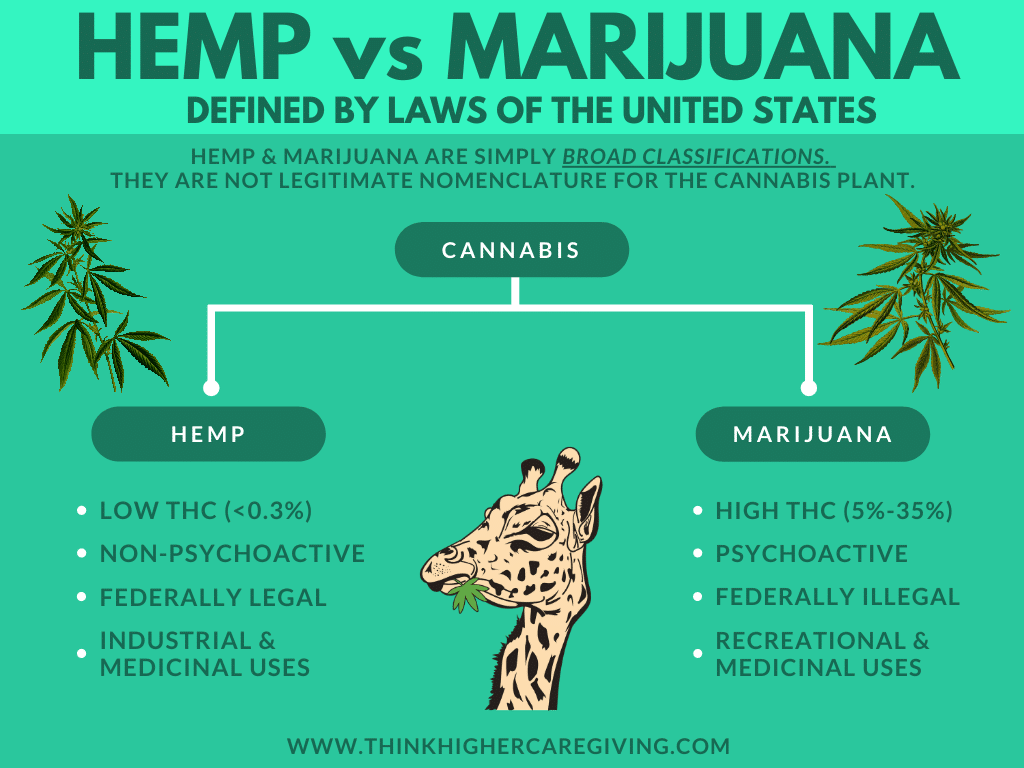
Cannabidiol(CBD) distillates can be obtained from Marijuana plants from time to time. However, this only increases the possibility that the distillate results in containing high levels of THC.
This can have a significant consequences due to how CBD is completely legal for consumption in all 50 states in the US, while THC is not.
CBD distillate extracted from hemp typically contains about 90 percent or more cannabidiol. The other 10 percent of the distillate is made up of other cannabinoids, and potential unwanted molecules (errors in the distillation process).
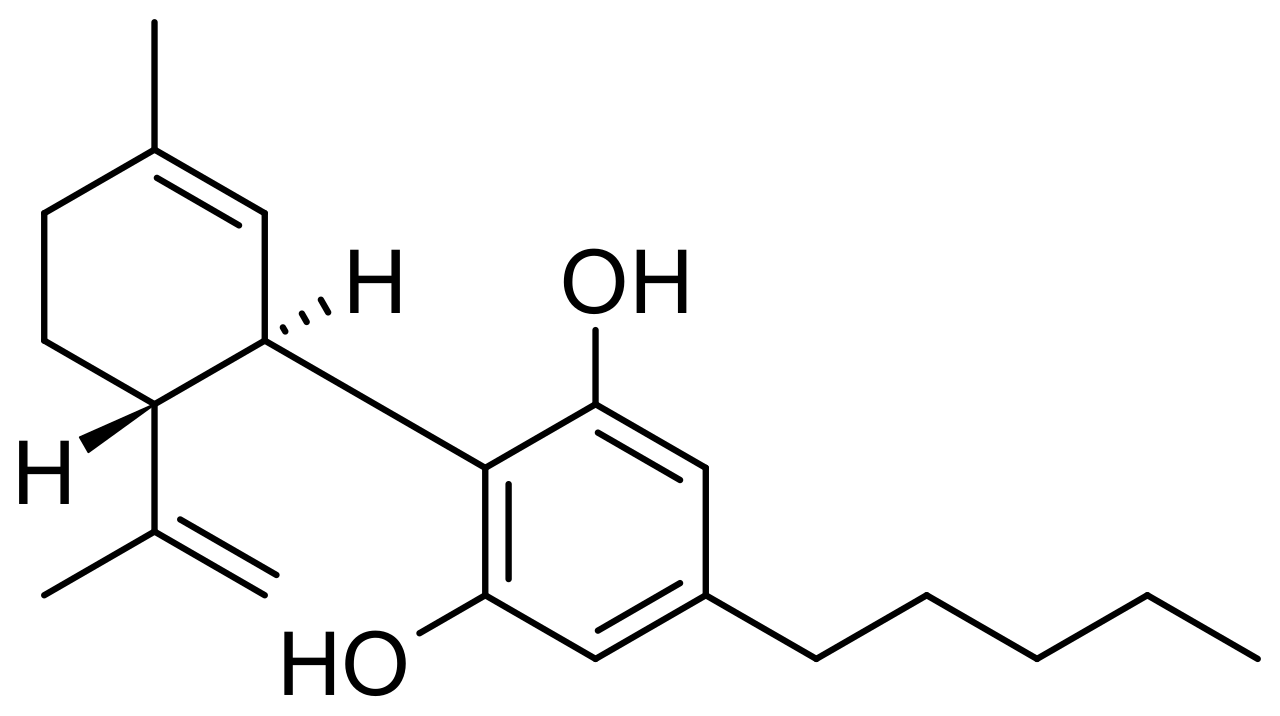
CBD Molecule
They are typically the second purest cannabidiol supplements available on the market stock. The enhanced purity offers your end customers the luxury of not consuming much to start enjoying all of its essential benefits.
Distillates are perfect in the manufacturing of capsules, vape oils, and edibles, tinctures, simply because of its purity. Distillates are also often refined even further to make the purest cannabidiol extracts on the market, isolates.
The Process
The goal of distillates is to produce a product that has a clean slate where we can infuse the desired terpenes for desired effects.
The distillation of cannabinoids, as stated above, applies to both CBD derived from hemp, as well as THC derived from Marijuana.
There is a reason enthusiasts in the cannabis community sometimes refer to cannabis distillate as “The Pure.” That’s precisely what it is, a product that’s virtually pure cannabinoids.
So How Are DISTILLATES Made?
Cannabinoids are refined and separated by the process of distillation at the molecular level. The goal of making cannabis distillate is to isolate cannabinoids like CBD and THC from unwanted impurities.
The whole procedure is made up of several refinement processes. The main steps of the distillation of cannabinoids are explained below;
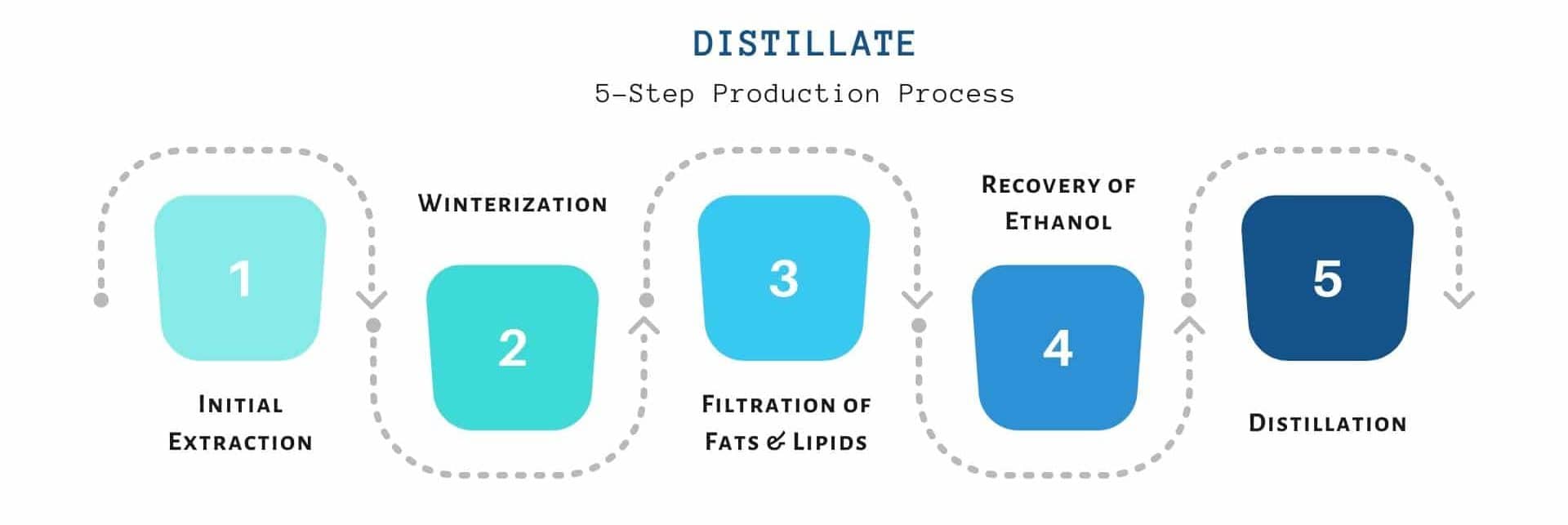
The Initial Crude Extraction of Resin from Hemp plant
The first step of distillation, the same as any cannabinoid extraction, is to extract the cannabinoids from the raw cannabis plant.
The extraction and distillation of cannabinoids are incredibly similar, as they both separate compounds.
In the initial crude oil extraction method, either solvents or physical methods (like rinsing and sifting) are used to separate the compounds.
However, there is a large difference between the two.
Distillation is separating compounds based on boiling points while extraction is separating compounds based on the solubility of the extraction solvent.
In the cannabis industry, extraction involves the collection of oils from the plant material.

Oleoresin Credit: Ocpharm.com
In contrast, distillation describes the process of refining the extracted oil into required constituents, which can be later incorporated into marketable goods.
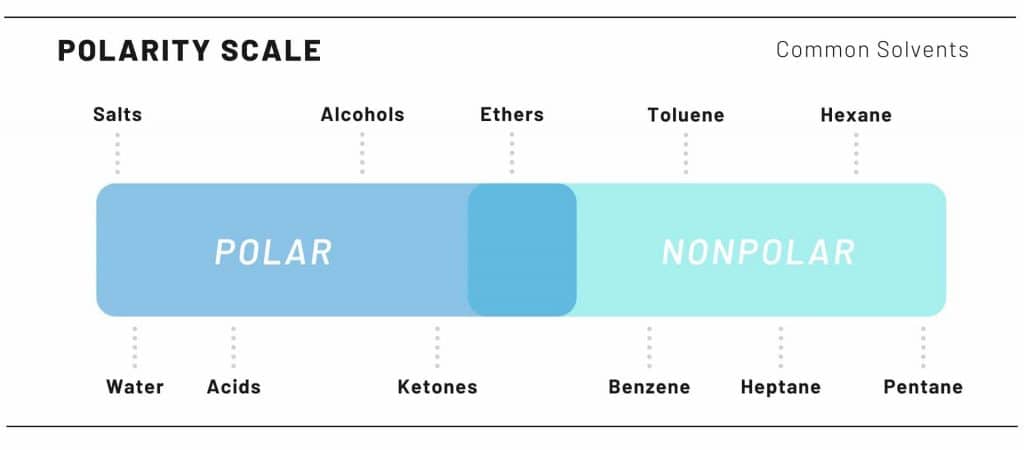
Cannabis crude oil extractions are done by polarity. Remember chemistry class? The saying “like attract likes”? Well that is precisely how solvents work to extract the cannabinoids.
Cannabinoids are nonpolar. Therefore, nonpolar solvents are used to pull the cannabinoids, leaving behind, unwanted, polar molecules. These polar molecules are things such as chlorophyll and potential water.
The polar solvents used for extractions ranges from extractor to extractor, like an artist only using a certain type of writing utilize.
Some of the more polar solvents used are Butane, Propane, & Pentane.
Alcohols & polar solvents can be used, however more unwanted product results in the final product.
The first extraction produces a product known as oleoresin, which is further refined.
The oleoresin, produced in this process, can be summed up as the concentrated cannabinoids, in addition to, all the flavoring ingredients soluble in the particular solvent used, so that it is much closer to the original…odor and flavor.
Some impurities are still present in the extracted oil – fats, lipids, and several other unwanted compounds. These compounds are removed within the next step, the winterization process.
Winterization of Oleoresin to Remove Impurities
Of course, the initial extraction process yields an extract that is full of the desired cannabinoids. But, it also contains many impurities that are unnecessary and could be harmful upon consumption.
Impurities also prevent the further steps in the distillation processes from making a high quality final product.
Winterization is conducted to remove unwanted impurities efficiently.
The winterization process is very similar to baking a chicken: In baking a chicken, the excess grease and juices (aka impurities) drip down into the pan and then thicken when cooled.
In the winterization process, the crude extract and ethanol solution is passed through a filter. Here, the fats and lipids are removed. The remaining ethanol solution is then typically recovered, done using a rotary evaporation technique.
The process starts by mixing the initial crude extract with pure ethanol.
This solution is placed in a freezing environment for roughly 24 to 48 hours at this point. During the freezing phase, most of the unwanted impurities solidify. 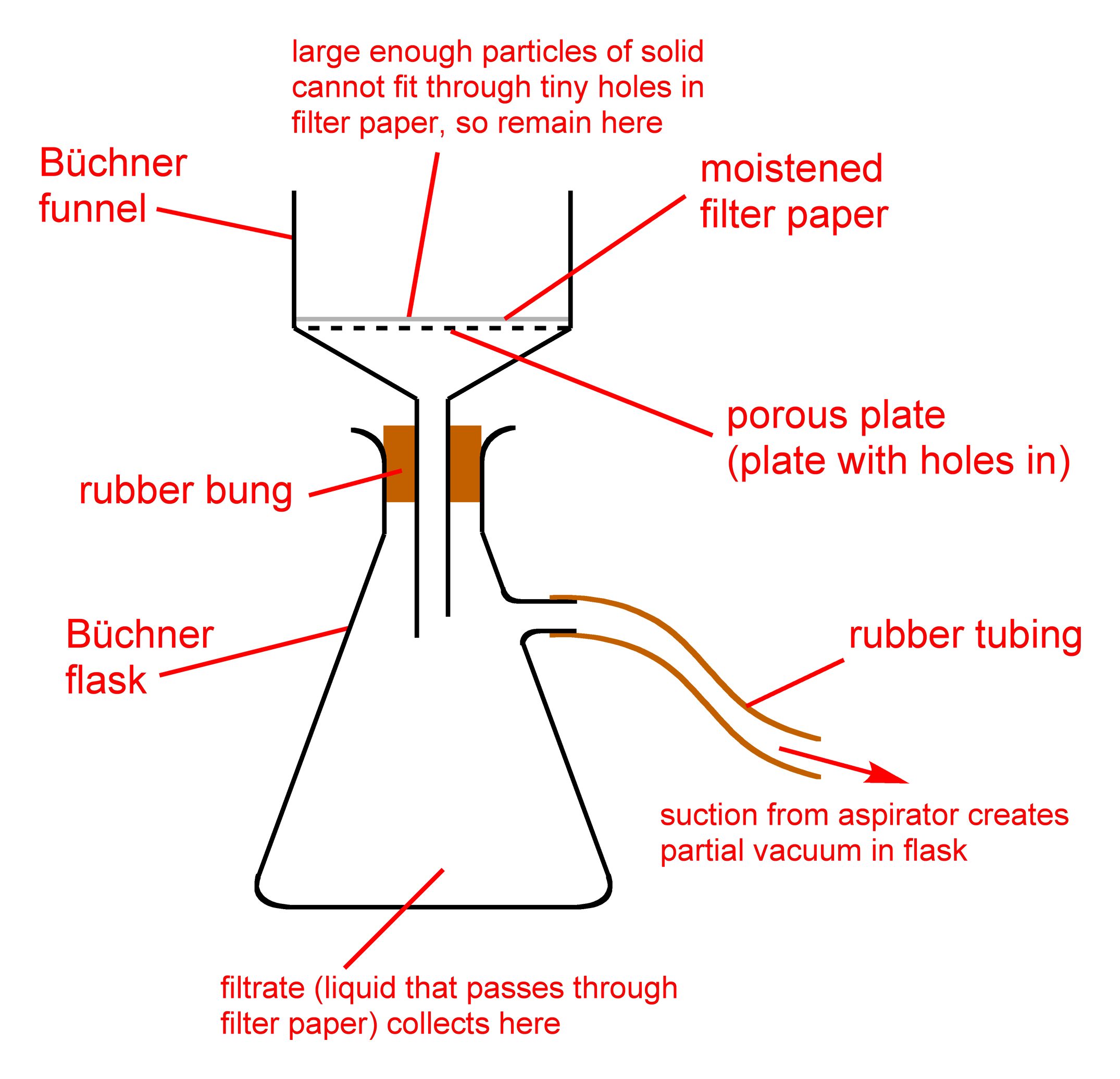
The extremely cold crude extract and ethanol solution is then passed through a filter. Fats and lipids are caught in the filter, while the cannabnoid rich ethanol passes through. This filtration process is normally performed using a simple buchner funnel.
Recovery Of Ethanol
After the fats, lipids and other minor impurities are filtered out, the ethanol is removed/recovered. Ethanol removal is typically done using a rotary evaporator.
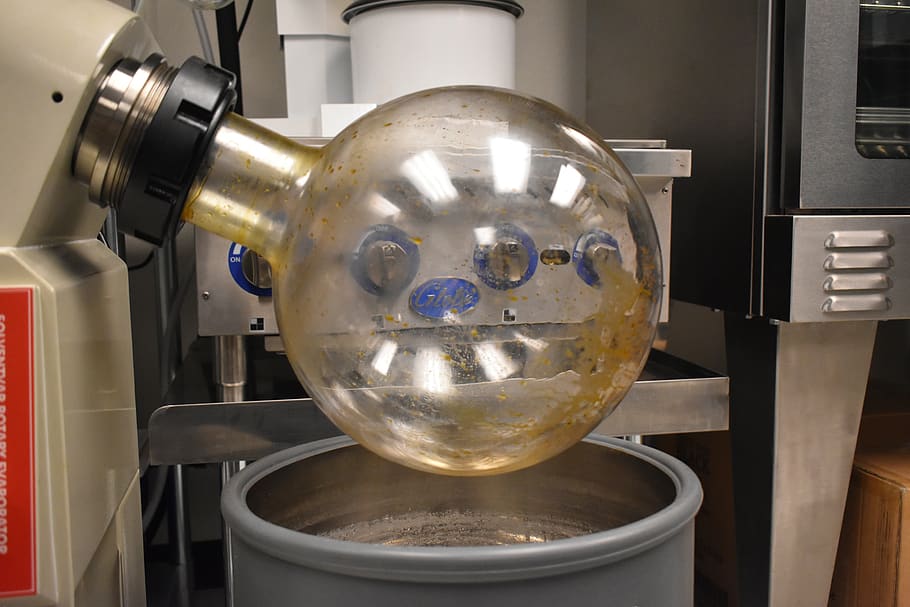

Rotary Evaporation will remove a majority of the ethanol initially added. “One reason that rotary evaporation is favorable for this technique is that the process is efficient with minimal labor. Because the ethanol can be reclaimed once extracted in a rotary evaporator, a manufacturer significantly reduces overhead costs.”
The final product is a resin containing the desired cannabinoids, other minor cannabinoids, terpenes, and antioxidants.
Decarboxylation of Cannabinoid acids
Cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant are always locked in an acidic form.
Cannabinoids generally has more benefits when changed to a more active and stable state. The is accomplished through the decarboxylation process.
Decarboxylation involves heating the solution to the right temperatures until all of the desired compounds are converted, making them activated.
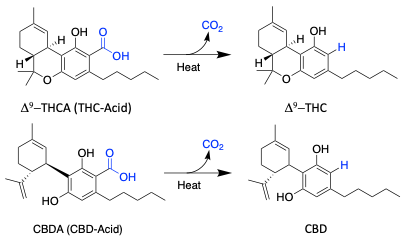
Credit: https://www.medisenol.com/science-of-extraction
Decarboxylation of the oleoresin is done to minimize the amount of time during the actual distillation step.
However, decarboxylation can occur during the distillation process.
Either done before or after, does not seem to matter, but due to the high temperatures required during distillation, 100% of distillate is decarboxylated. Making them perfect to cook with.
Distillation
The distillation process is a separation technique that uses heat, steam, and vacuum pressure to separate compounds in a solution from each other.
Extractors can collect the compounds individually by influencing the boiling points of each compound.

Credit: hightimes.com
In a normal cannabinoid distillation, flavonoids, terpenes, and other unwanted molecules are removed first, as they contain lower boiling points than cannabinoids.
The end product, distillate, is a golden yellow color with a viscosity that is higher than honey.
The distillation procedure can be run multiple times to get the distillates further refined.
It is important to note that there are several different forms of distillations, which are described below.
Simple Distillation Vs Fractional Distillation.
Simple Distillation
Distillations all have similarities in the fact that they both separate mixtures, using similar equipement. However, there are two main types of distillations which distillates are produced by.
The difference between simple and fractional distillation, at its core, is the number of times that the liquid is vaporized and condensed.
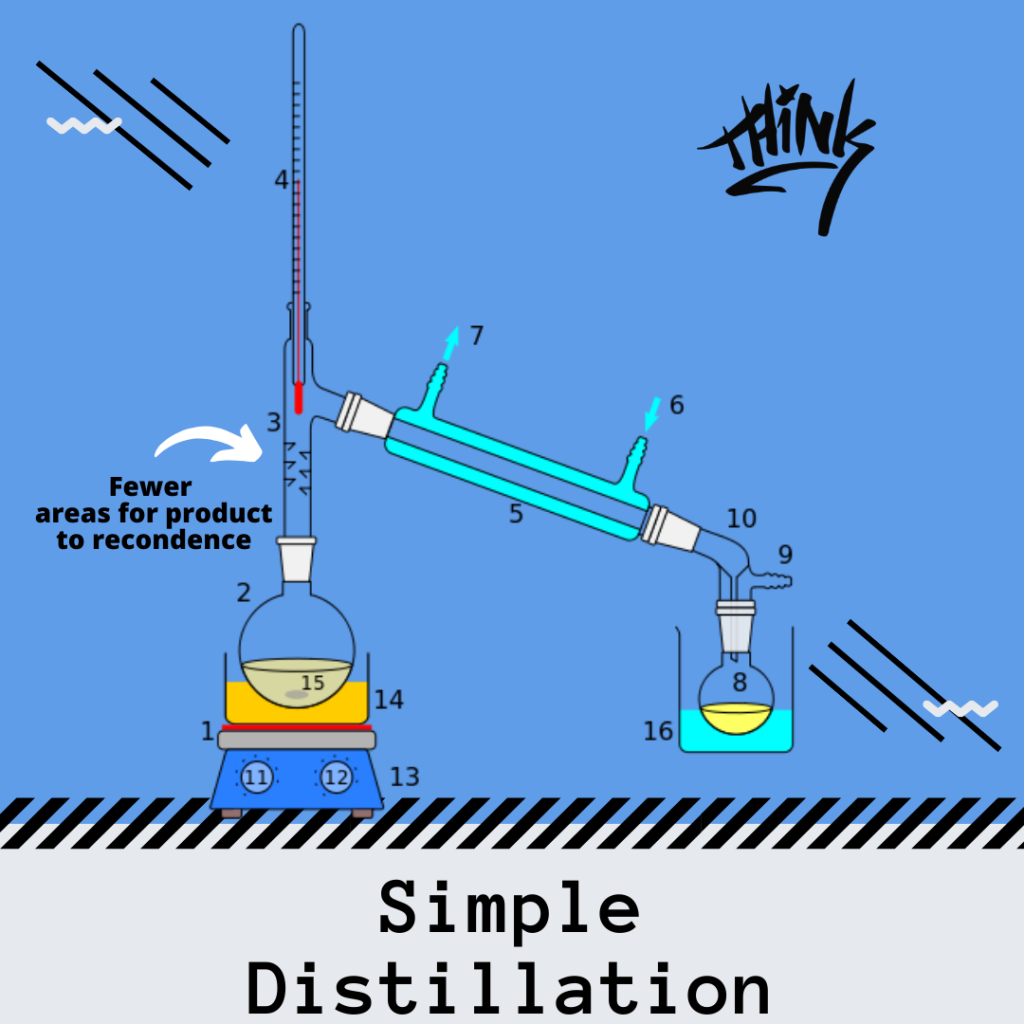
During simple distillation the liquid condenses once. Therefore a large difference in boiling points of the two liquids must be achieved to make an efficient distillation.
For example, simple distillation is often used to separate the liquid substance from a solid substance.
Fractional Distillation
During fractional distillation, two or more cycles of distillation occur.
An additional piece of equipment is used during fractional distillation, a fractionating column. This fractionating column acts as an obstruction to the gases.

As material is heated and boiled, the “not pure enough” vapors condense on these columns, falling down until it is reheated by other rising gases. This process of heating, condensing, heating, is referred to as rectification. Rectification leads to better separations leading to a purer product.
The heating and condensing process occurs until the vapor can pass through all the “obstructions” in vapor form where it is eventually collected into a flask.
Fractional distillation is commonly used when the material being distilled contains molecules with boiling points that are similar to each other.
Due to the large number of molecules within the Cannabis plant fractional distillation is the main form used to produce distillate.
Different Fractional Distillation Setups

Credit: Labsociety
There are multiple different fractional distillation setups. Again some cater to speed while others cater to purity.
The popular setups for distillate production currently in the industry are:
- Short Path Wiped Film Distillation
- Short Path Distillation
- Spinning Band Distillation
For this article we will specifically describe the short path distillation setup.
What is short-path distillation?
Short-path distillation is a type of technique and apparatus. It’s a simple technique where the the short-path setup involves minimal travel distance for the vapors, hence the term short-path.
The technique is used in several types of industries and has been around for over 30 years in several production fields.
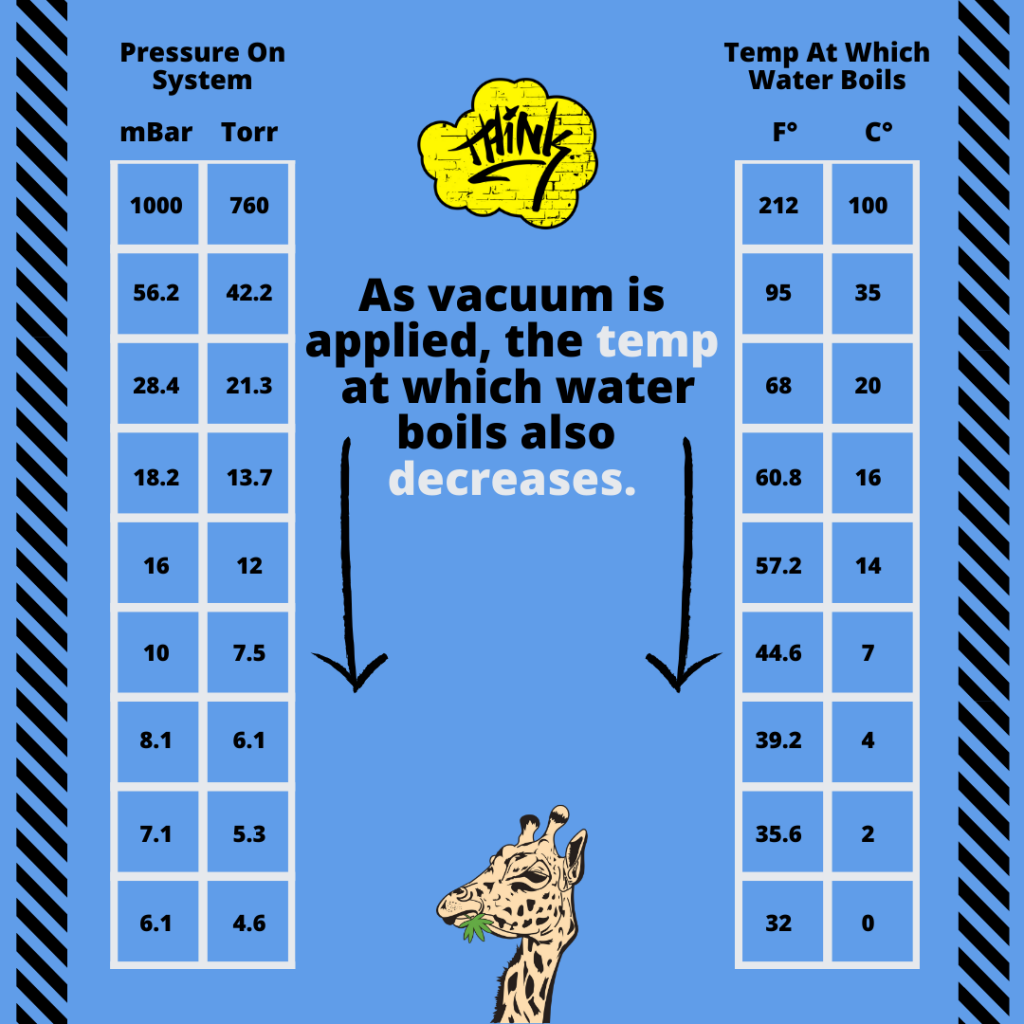
This distillation is completed under vacuum, which decreases the liquid’s boiling point.
Due to the decreased boiling point, it is an excellent method to be implored for unstable compounds at high temperatures or to purify small amounts of a compound.
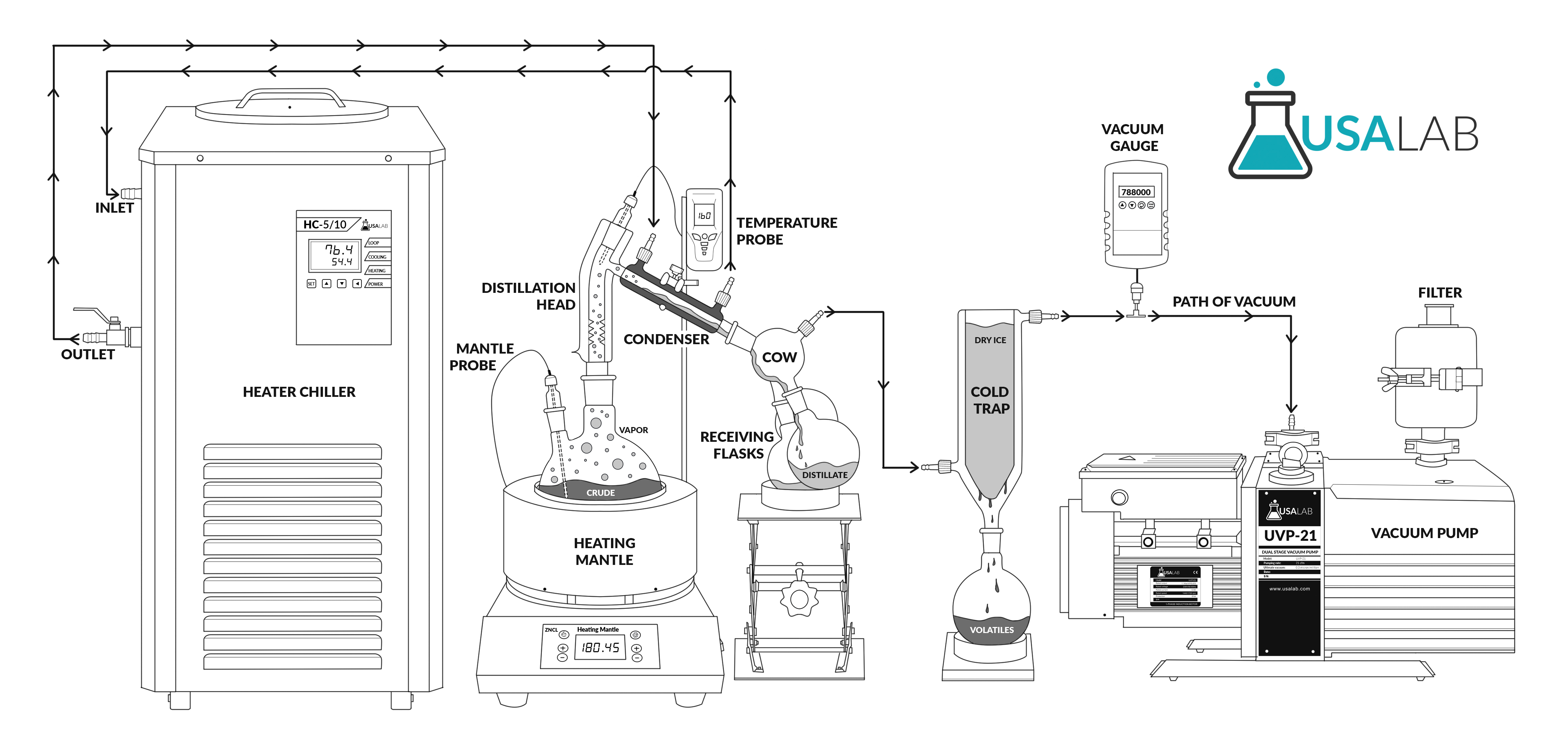
Credit USALAB
Once vacuum is applied, a flask containing the starting material is heated and boiled. As this material gradually heats up, the vapors climb the fractional column atop the flask.
As the vapors become purer and purer during the rectification stage, they eventually make their way to the condensing tube. The condensing tube is where the vapor fractions condense back into a liquid form.
The contents flow down a specific path to separate, desired flasks.
When is short-path distillation applied?
The general distillation processes in the laboratory can be elaborate and complex.
The short-path strategy utilizes glassware, which in turn, reduces potential loss of materials adhering to the inner surfaces of the apparatus.

The short-path distillation technique is employed where product loss can be expensive during production.
At an average price between $40-$70 per gram, the short path technique is a proper route to minimize costly losses.
For these reasons short path technique is a perfect fit for the distillation of cannabinoids.
All because of temperature?
The crucial part of purification by distillation is temperature.
Other physical chemistry properties contribute to the effectiveness and efficiency of the process, but the temperature is highly essential to achieving high yields of the desired products.
Defined specifically, temperature is just a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object.
A vacuum is often used to improve the process by allowing distillation at lower temperatures, thereby reducing the potential of altering the chemical composition of distillates.
It is important to note that a vacuum doesn’t affect temperature, however it will affect the TRANSFER of heat.
This way, the molecules are not subjected to heat for a long period of time, thereby reducing the potential of altering the chemical composition of distillates.
Short- path distillation, or other forms of fractional distillation is a very important step to get the end product, without terpenoids, flavonoids, and contaminates.
Contaminants are by-products like residual solvents and pesticides. Certain pesticides do share overlapping boiling points with some cannabinoids.
A very harmful and dangerous pesticide, Myclobutanil, has a boiling point of 205°C.
CBC and THCV both have a boiling point of 220°C or over.
Therefore subjecting myclobutanil ridden product to distillation will cause pesticides to get into the final product.
The final product then has to undergo post-processing techniques such using adsorbents during flash chromatography.
Solvent-based Vs Solventless Vs Solvent-free
The production of distillate is a bit different than the previous ways of producing cannabis concentrates such as wax, shatter, budder, and crumble. These “previous” extracts were primarily made via these two processes:
- The Solvent-based Extraction

- The Solventless Extraction
Like almost everything in the world, both extraction processes have their pros and cons. Note that neither of these methods results in pure and clean end solutions as distillation does.
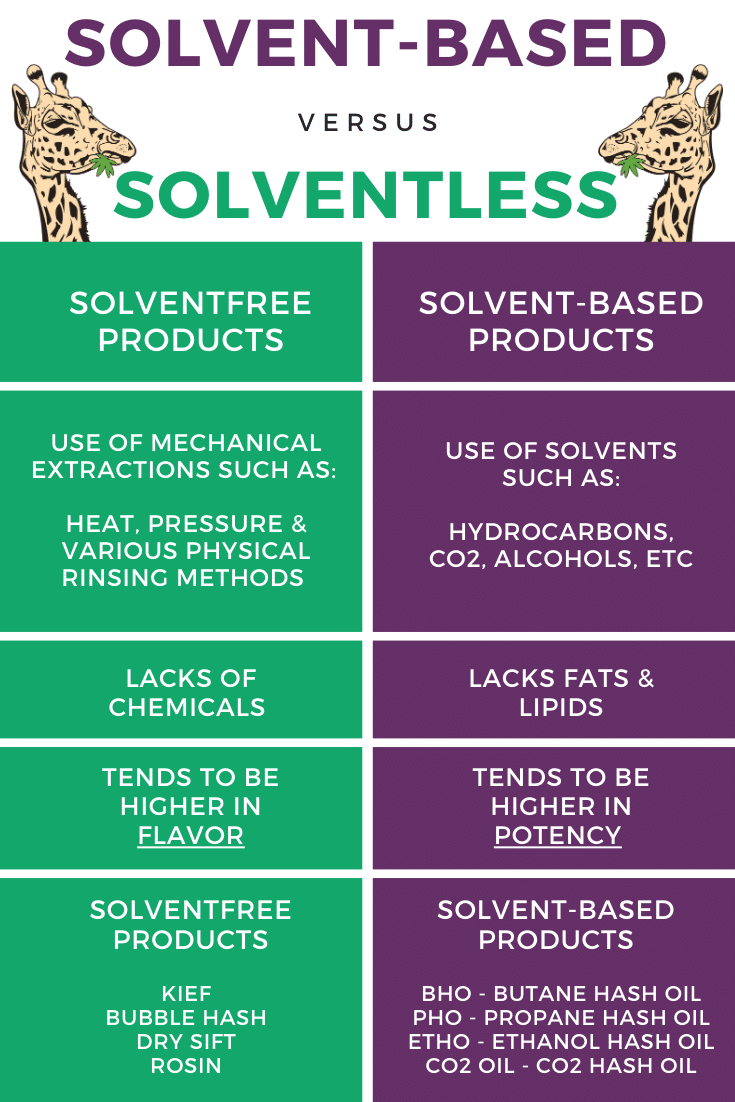
Solvent-Based Extractions
A solvent-based extraction uses solutions such as alcohol or butane to pull out the wanted compounds -such as terpenes, cannabinoids, and flavonoids- from the initial cannabis plant material. Wax, shatter, and other concentrates found here are made from this method.
Solventless Extractions
A solventless extraction uses heat, pressure, or various physical rinsing methods to collect the same desired compounds. These types of extractions yield concentrates, such as bubble hash and rosin.
Solvent-Free Products
Important to not confuse solvent-free products with solventless extractions. Solvent-based extraction products can be considered solvent-free products if they undergo post extraction procedures. These post extraction procedures remove all residual solvents, used in the original extraction.
What makes THC and CBD distillate so useful?
Distillates are cannabis in one of its purest forms. On average, cannabis distillates possess around 90 percent CBD and THC from hemp and Marijuana, respectively. The rest of the 10 percent comprises other cannabinoids, and various beneficial molecules.
Cannabis distillates high concentration is one reason why it’s one of the most effective cannabis products currently on the market.
Whether you’re a medical patient that uses CBD or THC for its therapeutic benefits or are merely interested in enjoying recreational cannabis, distillate brings a powerful, potent punch.
You can use far lesser amounts of product to get similar results.
CONS
Even as cannabis distillate is one of the purest forms, you would find that it isn’t without its drawbacks.
One criticism of cannabis distillate is by those that ascertain that it is the start of “engineered” synthetic cannabis. Part of this reason, is due to chances of distilling impurities such as pesticides along with the cannabinoids.
By far, the most significant criticism of this type of extracted concentrate is that it contains very few terpenes (if any) that work harmoniously with cannabinoids like THC, CBD, and others to create the entourage effect.
These thoughts, however, do not seem to stop the rising popularity of distillate products.
Cannabis distillate offers much versatility to produce various beneficial consumer products that fit a wide variety of individuals.


